S1
From The Eco-STEM Wiki
Structure S1: Provides clear goals/outcomes
Practices
- Great structure starts with clear goals. It is a good idea to review the learning goals of the course to ensure that they are clear, measurable and generate significant learning experiences.
Activities
- There are many tools available for instructors to use to design the learning goals and outcomes. L. Dee Feek's "What is Significant Learning?" can help instructors design learning goals in six categories: fundamental knowledge, application, integration, learning skills, caring, and human dimension. [1]
- To develop measurable learning outcomes, you can also employ Bloom’s Taxonomy, which is a system that divides analytical tasks and learning into different levels of difficulty. This link provides an overview of the original and revised taxonomies, as well as a list of action verbs [2]. Action verbs [3] are used to describe desired student activities. Another resource for Overview and history of Bloom’s taxonomy, with revisions, is here [4]. Here, you can find a helpful description of the different levels of Bloom's Taxonomy [5].
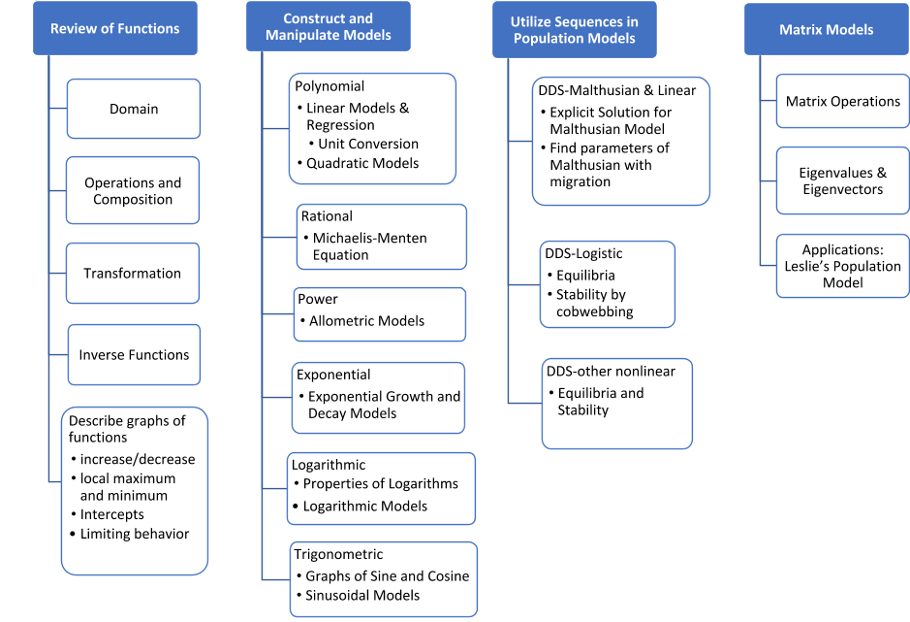
- After developing the learning goals/outcomes, it is good to articulate them with your students. One way to do this is to provide a visual syllabus. Here is an example:
Observable Behaviors:
S1.1: Provides purpose and learning outcomes of the lesson
S1.2: Places the lesson into the overall arc of the course
- ↑ Feek, L. D. What is Significant Learning? https://www.wcu.edu/WebFiles/PDFs/facultycenter_SignificantLearning.pdf
- ↑ Bloom's taxonomy: Revised levels, verbs for objectives. Valamis. (2022). https://www.valamis.com/hub/blooms-taxonomy
- ↑ Anderson, L. W., & Krathwohl, D. R. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing, Abridged Edition. Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon. https://www.uky.edu/~rsand1/china2018/texts/Anderson-Krathwohl%20-%20A%20taxonomy%20for%20learning%20teaching%20and%20assessing.pdf
- ↑ Armstrong, P. (2010). Bloom’s Taxonomy. Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching. https://cft.vanderbilt.edu/guides-sub-pages/blooms-taxonomy/
- ↑ Piggott, J. (2017). Bloom's Taxonomy. University of Cambridge: Faculty of Mathematics. https://nrich.maths.org/5826