Peer Observation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
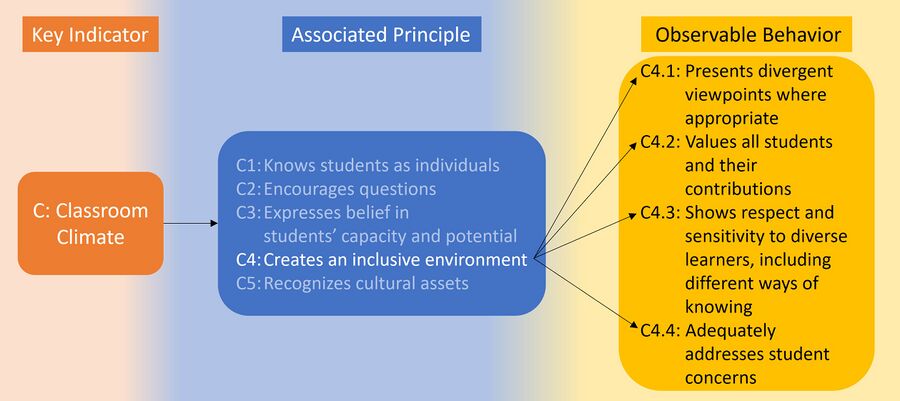
The process is built around the three key aspects, Climate, Structure, and Vibrancy. Each of these aspects has five associated principles, which in turn has associated behaviors that can be observed in a classroom. The image below shows an example of classroom climate. | The process is built around the three key aspects, Climate, Structure, and Vibrancy. Each of these aspects has five associated principles, which in turn has associated behaviors that can be observed in a classroom. The image below shows an example of classroom climate. | ||
[[File:Peerobservation structure.jpg|alt=Peer Observation structure|center|thumb|900x900px|Example of a Key Indicator, its Associated Principles, and Observable Behavior for one of the principles.]] | [[File:Peerobservation structure.jpg|alt=Peer Observation structure|center|thumb|900x900px|Example of a Key Indicator, its Associated Principles, and Observable Behavior for one of the principles.]] | ||
A summary of the principles and behaviors can be found in the '''[[Media: | A summary of the principles and behaviors can be found in the '''[[Media:Peer Observation Tool - Condensed.pdf|summary version of the observation tool]]'''. | ||
The observation process can be implemented flexibly, either as a peer observation process, or as part of the retention, tenure, and promotions process. The observation process is implemented in slightly different ways for the two different types of observations. The overall structure for both types consists of these three steps: | |||
[[File:Peerobservation flow.jpg|alt=Peer Observation Flow Summary|center|thumb|700x700px|Peer Observation Flow Summary]] | |||
The purpose of the ECO-STEM Peer Observation Tool is to get information on your class through a second set of eyes. When used with a peer for a peer observation, each instructor will observe the other. This is called '''peer observation'''. When used for an official observation, such as in the Retention, Tenure, and Promotion process, it is called '''evaluation observation'''. For further details on the implementation process, choose either '''[[Peer-Observation Instructions|peer observation]]''' or '''[[Evaluation Observation Instructions|evaluation observation]]'''. | |||
Latest revision as of 16:45, 15 August 2022
Eco-STEM Peer Observation Process
The main goal of the peer observation is to give feedback on the actual learning environment in the classroom and for the observed instructor to engage in a reflective process on their teaching.
The process is built around the three key aspects, Climate, Structure, and Vibrancy. Each of these aspects has five associated principles, which in turn has associated behaviors that can be observed in a classroom. The image below shows an example of classroom climate.
A summary of the principles and behaviors can be found in the summary version of the observation tool.
The observation process can be implemented flexibly, either as a peer observation process, or as part of the retention, tenure, and promotions process. The observation process is implemented in slightly different ways for the two different types of observations. The overall structure for both types consists of these three steps:
The purpose of the ECO-STEM Peer Observation Tool is to get information on your class through a second set of eyes. When used with a peer for a peer observation, each instructor will observe the other. This is called peer observation. When used for an official observation, such as in the Retention, Tenure, and Promotion process, it is called evaluation observation. For further details on the implementation process, choose either peer observation or evaluation observation.